
Change managers typically grapple with various forms of resistance during organizational change. This resistance can manifest as reluctance to embrace new processes, heated debates, and widespread employee anxiety.
The Satir Change Model, conceived by Virginia Satir, a family therapist and author, addresses these challenges. Initially designed for family therapy, the model offers a framework for understanding and improving how people adapt to significant and unforeseen changes within a business context.
Leaders and managers can leverage the Satir Change Model to gain insights into their teams’ responses to change.
After reading this guide, you will know:
- What the Satir Change Model is, as well as its five stages
- The pros and cons of using the Satir Change model
- The best ways to implement the Satir Change Model within your business
What is the Satir Change Model?
Unlike traditional change models, Satir’s approach uniquely focuses on the human aspect of change, acknowledging the deep emotional engagement required for effective transformation.
The model outlines four distinct phases individuals typically experience in response to change: the initial late status quo, followed by resistance, then a period of chaos, and finally, integration. A fifth phase, termed the new status quo, signifies the culmination of successful integration.
This framework sheds light on the varying dynamics of performance, emotions, and behavior throughout these phases, influenced by external and internal factors.
By comprehending the emotional and psychological dynamics at play, this model serves as a valuable tool in having a smoother change process, reducing friction, and enhancing overall adaptability within the business environment.
Versatile in its application, the Satir Change Model provides valuable insights into change’s psychological and emotional dimensions, personal or organizational.
What are the five stages of the Satir Change Model?
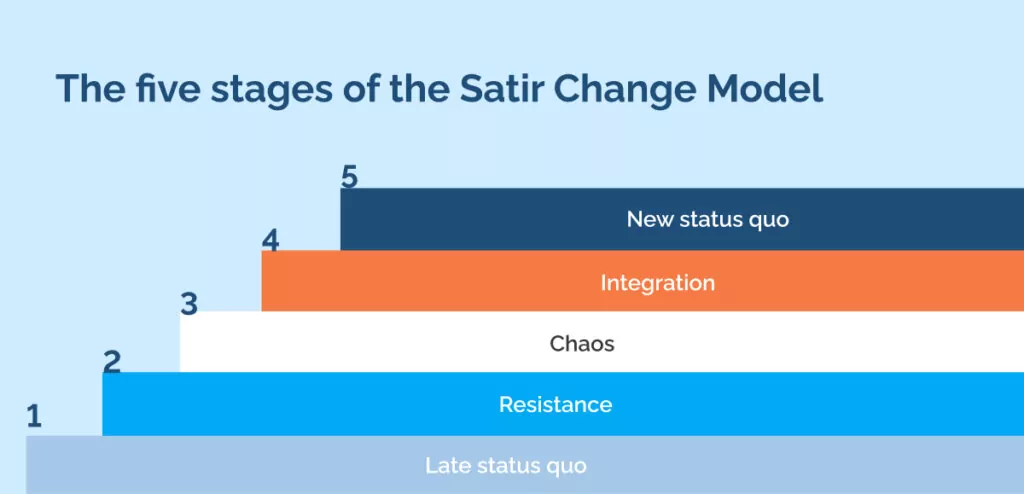
The Satir Change Model outlines a comprehensive process for individuals and organizations undergoing change, detailing five distinct stages:
1. Late status quo
In this initial stage, there’s a sense of comfort and routine in this initial stage, with established habits and predictable behaviors. Organizations may recognize problems, like declining sales or customer satisfaction, but stick to familiar methods, often resisting change because of a mindset of “this is how we’ve always done it.” Understanding this stage is crucial for recognizing the need to move beyond comfort zones towards meaningful organizational development.
2. Resistance
This stage marks the onset of resistance to change. Even though the need for change becomes more apparent, there’s often denial, blame, anger, or frustration. Individuals can view these changes as too disruptive or threatening. For instance, employees might resist new software, fearing job loss or difficulty in adapting.
Overcoming this resistance involves clear change management communication and involving people in the change process to foster investment and willingness.
3. Chaos
Characterized by confusion and a sense of disorder, this stage occurs when implementing changes. For example, introducing new software might lead to workflow disruptions and a period of adjustment. Recognizing this as a natural and temporary phase in the change process is vital, not a vital indicator of failure.
Providing support, adjusting plans, and maintaining clear communication can help navigate this stage.
4. Integration
In this phase, the benefits of change become apparent, and new methods are integrated into daily routines. A sense of stability returns, along with renewed purpose. For instance, a company may find improved efficiency with new software after initial chaos.
This stage calls for reinforcing changes, celebrating successes, and providing ongoing support to ensure continued adaptation and progress.
5. New status quo
The final stage signifies the full integration of changes, establishing a new norm. The changes are no longer consciously noticeable, and improvements become part of everyday operations.
Continual monitoring and adjustments ensure these changes meet long-term organizational needs. Recognizing the new status quo as a dynamic state of continuous improvement is essential for fostering an organizational culture of ongoing change and development.
What are the advantages of the Satir Change Management Model?
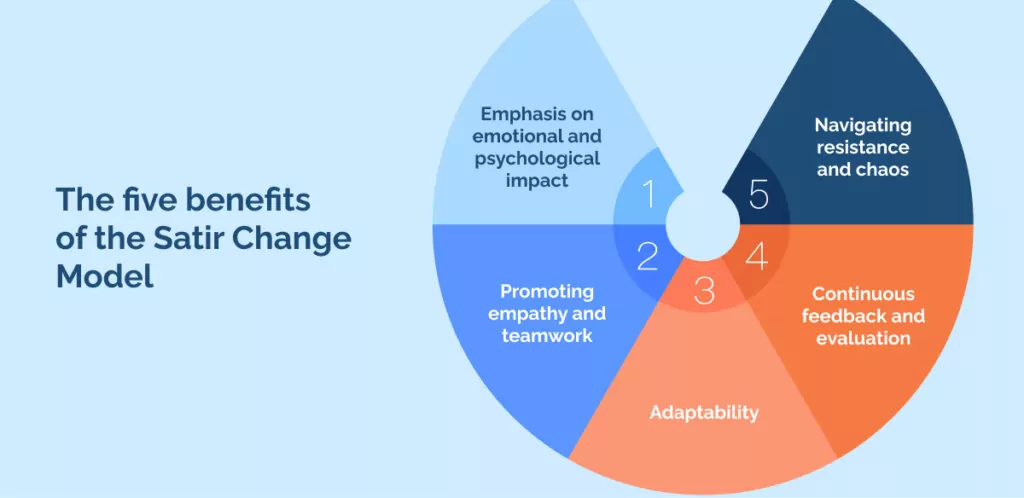
The Satir Change Management Model offers a range of benefits, making it an attractive option for organizations navigating the complexities of change. Its key advantages include:
Emphasis on emotional and psychological impact
This model prioritizes understanding change’s emotional and psychological effects on individuals and groups. Acknowledging the human side of change aids organizations in addressing resistance and improving employee engagement and ownership.
Promoting empathy and teamwork
Central to the Satir Model is the role of empathy and teamwork in effecting change. The model cultivates a shared sense of responsibility and common objectives by encouraging involvement from employees and stakeholders and championing open communication and collaboration.
Adaptability
The Satir Model’s strength lies in its adaptability to various organizational environments and the change management life cycle. It suits minor and significant changes, offering customization options to align with specific organizational needs and objectives.
Continuous feedback and evaluation
An ongoing process of feedback and evaluation is integral to the Satir Model. This continuous monitoring allows organizations to adjust and refine their strategies, ensuring the long-term effectiveness and sustainability of the change initiatives.
Navigating resistance and chaos
The model provides a structured approach to resistance and chaos, common byproducts of change. Understanding the different stages of change and their associated emotional and behavioral patterns enables organizations to anticipate and manage these challenges more effectively.
What are the challenges associated with the Satir Change Model?
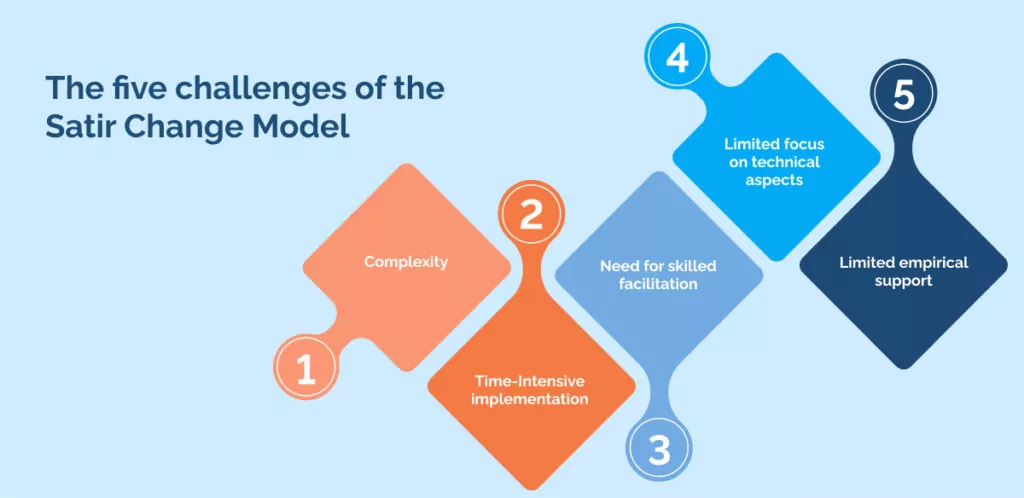
The Satir Change Management Model, though beneficial in many aspects, has its own set of potential drawbacks and limitations that organizations should consider. These include:
Complexity
The model’s intricate nature and multiple stages and elements can pose challenges. This complexity may make it difficult for some organizations to comprehend and implement the model entirely.
Time-Intensive implementation
Particularly for larger-scale changes, implementing the Satir Model can be time-consuming. Its emphasis on collaboration, ongoing feedback, and thorough evaluation can extend the duration of the change process, which might be problematic for organizations with strict deadlines or limited resources.
Need for skilled facilitation
Effective use of the Satir Model requires experienced facilitators. The model’s success hinges on the ability of a training facilitator to guide the change process, manage resistance and chaos, and encourage collaboration and empathy among employees. Organizations needing more skilled facilitators might find the model less effective.
Limited focus on technical aspects
The model primarily addresses the human side of change, potentially overlooking significant technical or process-oriented aspects. Organizations may need to integrate additional methodologies or frameworks to complement the Satir Model for heavy technological changes.
Limited empirical support
Despite its widespread application, there is a need for more empirical evidence to underpin the effectiveness of the Satir Change Management Model. Its suitability and efficacy may vary across different organizational contexts and types of changes, and it might only sometimes be the optimal choice for some scenarios.
How to apply the Satir Change Management Model within your company
Organizational leaders and change managers can adeptly navigate their teams through the stages of the Satir Model for effective change management in the following ways:
1. Managing the late status quo stage
At this initial stage, transparent and open communication is critical. Leaders should explain the reasons and necessity for change, emphasizing its benefits for the organization and the employees.
This stage involves:
- Highlighting the need for change by pointing out risks and opportunities
- Articulating the vision and core values linked with the change
- Discussing the impact of the change on individuals and the organization, highlighting any skills gap
- Defining and tracking the success of the change with specific metrics
- Conducting thorough stakeholder analysis
- Planning and executing effective communication strategies
2. Managing resistance
Leaders must approach resistance with empathy, understanding, and effective feedback. Identifying potential reasons for resistance and encouraging open communication will help manage this phase.
Strategies include:
- Engaging in transparent communication to foster self-advocacy among employees.
- Sharing feedback and addressing concerns and doubts about the change.
3. Managing chaos
During this tumultuous stage, leaders should anticipate reduced productivity and engagement.
Key actions include:
- Implementing change management training and mentoring programs to help employees understand and adapt to the change.
- Regularly share feedback and lead by example to guide the team.
- Monitoring productivity and engagement metrics.
- Helping employees set realistic goals and providing guidance.
- Encouraging empathy and optimism in the workplace.
- Clearly defining expectations and performance KPIs.
- Presenting the change as a career advancement opportunity.
4. Managing integration
This critical phase needs careful handling to prevent a regression to chaos.
Leaders should:
- Encourage active participation in the change process and learning engagement.
- Recognize positive behaviors and achievements, as employee recognition is vital for morale.
- Understand that appreciation can significantly motivate employees to embrace change.
5. Managing the new status quo
In the final stage, it’s important to solidify the change as part of the organization’s new normal.
Leaders should:
- Ensure the change is fully integrated and sustained within the organization.
- Plan for and implement incremental improvements.
- Celebrate the successful workplace transformation to maintain high morale.
- Continuously assess if new skills, hires, leadership changes, mergers, acquisitions, or technological investments are needed to optimize the outcomes of the change.
- Effectively guiding teams through these stages requires strategic planning, empathetic leadership, and continuous engagement with the team.
Key takeaways related to the Satir Change Model
The Satir Change Model, often called the 5-stage change model, is a distinguished change management method widely adopted by organizations for assessing and executing transformations.
Developed by Virginia Satir, a notable American family therapist, this model’s main philosophy is that change managers must optimize outcomes throughout any change process.
Distinct from other change management strategies, the Satir Change Model involves observing and tracking performance metrics during the implementation of change rather than directly influencing them.
Despite its limitations, one can celebrate this model for its effectiveness in providing a business change manager with insights into how their teams adjust to change. This understanding allows for more efficient and reassuring management of the change process.
A critical aspect of this model is the recognition that team members may progress through the stages at varying paces and that emotional responses can overlap or revert to previous stages if a business does not resolve issues adequately.
The Satir Change Model is instrumental in advancing the change process by guiding staff through each stage. It also serves as a valuable tool for managers in the planning stages of change, reminding them to define a change’s impact on staff, especially in the short term.
This awareness enables managers to plan more effectively, providing necessary support and accommodations to facilitate smoother transitions.
WalkMe Team
WalkMe spearheaded the Digital Adoption Platform (DAP) for associations to use the maximum capacity of their advanced resources. Utilizing man-made consciousness, AI, and context-oriented direction, WalkMe adds a powerful UI layer to raise the computerized proficiency, everything being equal.


